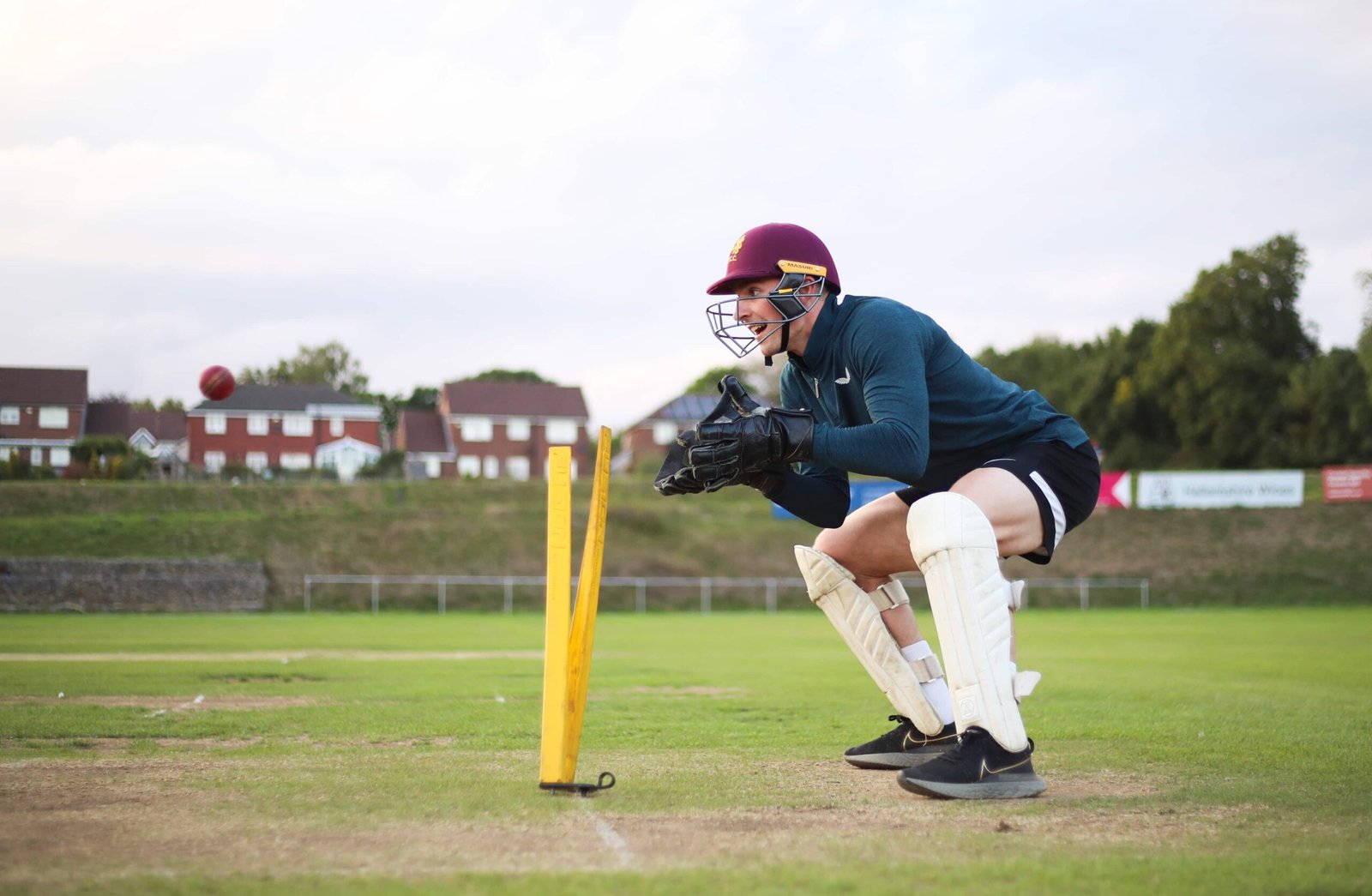
The wicket-keeper is a crucial player on the fielding team in cricket, positioned behind the stumps guarded by the batsman. This role is vital for both defensive actions and achieving dismissals. The wicket-keeper’s main duties include catching balls that bypass the batsman, whether delivered by the bowler or edged off the bat. They also aim to stump batsmen by dislodging the bails when the batsman is out of their crease and not attempting a run, and to effect run-outs by collecting throws from fielders and breaking the stumps before the batsman reaches the crease.

According to MCC Law 27, the wicket-keeper is the only fielder allowed to wear gloves and external leg guards. These accessories are considered part of the wicket-keeper’s body under Law 28.2 (Fielding the ball). If their actions or positioning make it evident to the umpires that they cannot perform their standard wicket-keeping duties, they lose the right to these protections and their designation as a wicket-keeper under Laws 33.2 (A fair catch), 39 (Stumped), 28.1 (Protective equipment), 28.4 (Limitation of on-side fielders), and 28.5 (Fielders not to encroach on the pitch).
Beyond technical responsibilities, the wicket-keeper is central to the team’s overall strategy and energy on the field. They often motivate and guide bowlers and fielders, playing a key role in maintaining team morale. In some cases, the wicket-keeper also takes on leadership roles as captain or vice-captain, offering valuable tactical input. Their ability to minimize runs and maximize dismissals makes the wicket-keeper indispensable to a team’s success. For more information.